As part of our mental health and wellbeing deep dive, we learnt a lot about what our current healthcare system does well, but also the cracks which no-longer suit our fast-paced tech-driven lives. As part of this we’ve imagined what good would look like 10 years in the future.
What the system does well
There have been significant advances in our healthcare system over the past few centuries. Vaccines (1796 by Edward Jenner1), antibiotics (1928 by Alex Fleming2) and innovations in surgical processes (such as hand hygiene – not until the 1870s3) were life-changing for humanity. As medical science advanced, science began to look deeper into specializations, and we became incredibly good at treating acute diseases4.
From a policy perspective, Australia has one of the world’s leading healthcare systems. Medicare makes basic healthcare free and accessible to most of the population.
Furthermore, the Covid pandemic accelerated the adoption of telehealth, it’s use increased >10 fold over the course of a month in 20205. This has increased accessibility of healthcare services for rural patients and those with disabilities, for whom traditional face-to-face visits aren’t accessible.
Where things fall apart
Whilst there are gaps within each specific niche, we’ve identified three major cracks in our current healthcare system:
• Chronic diseases
• Mental health
• Femtech
Chronic vs acute
Whilst acute diseases, where the physician is truly the expert, are very well treated, more complex multi-system illnesses have fallen between the over-specialized cracks. In particular 45% of the adult population has a chronic illness6 where the patient is the most important source of information7. These illnesses don’t fit neatly into one specialization and require multi-disciplinary care. Specialists tend to see every problem as their own segment. This means longer diagnosis times, misdiagnoses, overprescribing medicine, and often segmented care with only the patient aware of the full information set. Patients (majority having not studied medicine), don’t know what’s most relevant, and are often given the rabbit hole chase of seeing various specialists.
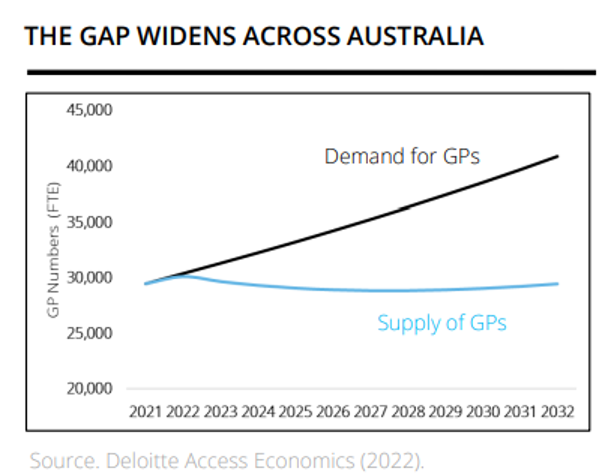
Whilst GPs are positioned as the “backbone” of the Australian healthcare system, it is difficult for them to fully assess the data needed for a chronic illness in a standard 15 minute consultation. In fact, GPs already spend 34-50% of consultations actively managing chronic conditions8. This problem is only set to expand with a forecast 38% increase in demand for services by 2032 driven by an ageing population coupled with an expected 4% decrease in GPs9. We need better systems and data analysis to let GPs perform this critical function, and to transition to patients being the center of their own care.
Mental health
Covid has stretched the healthcare system and this has been worst felt in mental healthcare. We have a huge gap in psychologists available, and children are experiencing more mental health issues today than previously. In 2018-2019 15.1% of adolescents experienced a depressive episode, and anxiety or depression was diagnosed in 8.4% of children aged 6-17 in 2011-2012 (as compared to 5.4% in 200310).
This is such an acute gap in our healthcare system that we’ve developed a whole theme around investing in mental health and wellbeing startups.
Femtech
FemTech is still catching up from 1993 when the FDA lifted its guideline to allow for women to be included in clinical trials11, and biases, particularly in pain management (perceivers under-estimate female patients’ pain compared to males’ pain12), still affect women and people of colour13. These outcomes are worst felt in marginalized demographics and fields such as gynecology (average 7.5 years to diagnose endometriosis14, 1/3 women reporting >2 years to diagnose PCOS15) and obstetrics.
There’s a clear investment and R&D gap that needs to be closed in terms of including women in medical trials and adjusting recommendations around female bodies. Conditions such as heart diseases, osteoarthritis, cancers, strokes and autoimmune diseases present in women differently and pose considerable health risks16. We need to have a healthcare system that addresses all individuals specific needs.
How we’d like 2033 to look
In order to service the nearly 1 in 2 people with chronic illness, we envision patients being at the center of their care journey, and data bridging gaps to medical intervention, we love the work Abby is doing in this space. We imagine a more interconnected health-care system with holistic care that is able to treat both acute diseases, and chronic illness. We imagine data at the center with algorithms analyzing the full healthcare picture of an individual and sending them to relevant specialists over time.
We imagine mental health care incidents decreasing, especially in children, with more knowledge and preventative treatment, such as an increased focus on resilience.
We imagine an even world where medications and medical interventions are customized and all population segments have equal access to quality, personalized care.
What this means
We love data and businesses that are placing the patient at the center of their own care. We look to data for preventative mental health care and solutions that are scalable to improve accessibility. We look for things that avoid the rabbit hole chase – wasting patient and physician time – to create optimal and efficient outcomes. We look for solutions that connect mind and body and treat the patient as a holistic person – not one with an isolated diseased organ.






